In 2025, digital banking regulations Nigeria 2025 saw major updates that reshaped the country’s fintech landscape. The Nigerian government passed the Investment and Securities Act (ISA) 2025, formally recognizing digital and virtual assets as securities. This new legal framework integrates cryptocurrencies, digital wallets, and other virtual assets into Nigeria’s financial system, paving the way for safer and more transparent digital banking.
This article explores the digital banking regulations Nigeria 2025 in detail, including its key components, effects on stakeholders, compliance requirements, and what the future holds for Nigeria’s fintech sector. We will also provide actionable insights for banks, fintech companies, and consumers navigating these changes.
Evolution of Digital Banking Regulations in Nigeria
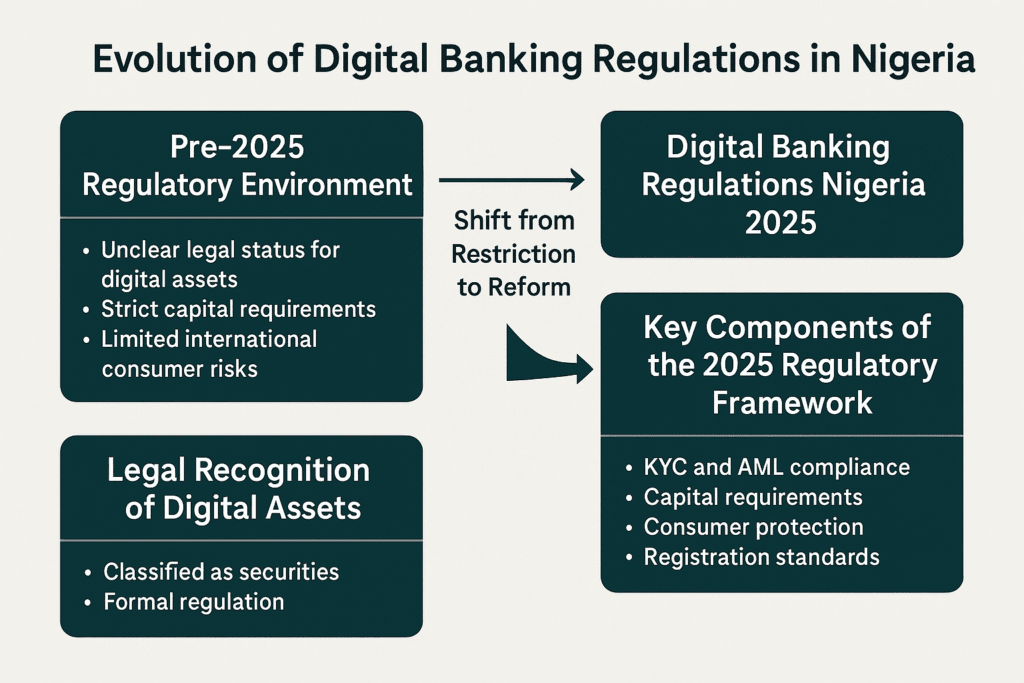
Before 2025, Nigeria’s fintech laws were often unclear. Digital assets like cryptocurrencies operated in a legal gray area, leading to uncertainty for businesses and users. However, with the enactment of the Investment and Securities Act (ISA) 2025, digital assets now hold official recognition under Nigerian law as securities. This landmark move aligns Nigeria with global financial centers such as Singapore, Switzerland, and Canada.
The ISA 2025 requires all Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) to follow strict transparency rules. These include Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) measures, which reduce fraud and protect consumers. VASPs must also maintain a minimum paid-up capital of ₦500 million and hold a fidelity bond to cover 25% of that amount.
This evolution shows Nigeria’s commitment to growing its fintech ecosystem under robust legal frameworks. It also helps attract both local and international investments by reducing risks.
Pre-2025 Regulatory Environment
Before the ISA 2025, fintech firms in Nigeria faced several challenges:
- Unclear laws: There was no clear legal status for digital assets.
- Strict capital requirements: Firms needed ₦500 million capital and insurance.
- Limited international compliance: Companies struggled to meet global standards like the FATF guidelines.
- Consumer risks: Without clear protections, consumers were exposed to scams and unfair practices.
While fintech firms were required to comply with general rules such as KYC and AML, many lacked formal guidance specific to digital banking. The absence of a clear framework slowed industry growth and innovation.
Shift from Restriction to Reform

The introduction of digital banking regulations Nigeria 2025 marked a turning point. The ISA 2025 legally recognized virtual assets as securities, requiring digital asset providers to:
- Register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Disclose business details transparently
- Comply with KYC and AML/Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) rules
- Maintain at least ₦500 million in paid-up capital
- Hold insurance for 25% of their capital
These reforms create trust, encouraging more Nigerians and investors to participate in digital finance.
Key Components of the 2025 Regulatory Framework
The 2025 regulations include several important elements:
| Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Legal recognition of digital assets | Virtual assets classified as securities under Nigerian law | Brings clarity and formal regulation |
| KYC and AML compliance | Strong customer identification and anti-fraud measures | Protects consumers and reduces financial crimes |
| Capital and fidelity bond | ₦500 million minimum paid-up capital and 25% insurance | Ensures operational stability of digital asset providers |
| Consumer protection | Clear loan terms, privacy safeguards, and complaint mechanisms | Safeguards users and builds confidence |
| Registration requirements | VASPs must register with SEC and report quarterly | Promotes transparency and accountability |
| Digital exchange standards | Strict rules for securities and virtual asset exchanges | Maintains market integrity and security |
These components aim to balance innovation and safety within Nigeria’s growing digital economy.
Virtual Assets and Their Regulation
Under Section 357 of ISA 2025, securities include virtual assets, commodities, and investment contracts transferable electronically. This broad definition opens the door for many digital products to fall under Nigerian regulation.
VASPs in Nigeria must meet the following:
- Submit detailed disclosures about operations
- Maintain the ₦500 million capital and fidelity bond
- Follow KYC and AML/CFT rules strictly
Following standards set by authorities such as Swiss FINMA, Nigerian regulators aim to foster responsible growth in digital finance.
Consumer Protection Measures
Nigeria’s regulators have introduced robust consumer safeguards:
- The 2019 Consumer Protection Framework ensures transparency and fair treatment.
- The Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Commission (FCCPC) Digital Lending Rules address exploitative lending and protect personal data.
- The Central Bank of Nigeria requires all lending institutions to hold licenses and follow risk-based supervision, including cybersecurity and privacy standards.
These protections are vital as digital banking grows in Nigeria.
Innovation in the Banking Sector
Nigeria’s fintech scene is booming. Digital wallets, mobile payments, and digital lending have grown rapidly. The Non-Resident Bank Verification Number (NRBVN) allows Nigerians abroad to open bank accounts remotely, boosting diaspora financial inclusion.
Also, the Open Banking Nigeria initiative helps banks and fintechs share data securely, fostering innovation and better services.
Learn how Digital Wallets Empower African Economies.
Impact on Stakeholders
The new digital banking regulations Nigeria 2025 benefit various groups:
| Stakeholder | Impact |
|---|---|
| Investors | More confidence and protection encourage investment |
| Banks | Must upgrade systems to comply with KYC, AML, and ISA 2025 |
| Digital asset firms | Clear rules for operation and growth |
| Consumers | Safer financial products and easier complaint resolution |
| Government | Stronger economic growth and financial inclusion |
Banks and Financial Institutions
Banks must register with the SEC and follow ISA 2025 rules. They are also adopting Open Banking APIs to improve services and interoperability.
These efforts align with global standards like Basel III, helping Nigerian banks compete internationally.
Check out the Neobank vs. Traditional Bank comparison.
Digital Asset Providers
Digital asset firms must:
- Register with the SEC
- Follow KYC and AML/CFT rules
- Maintain capital and fidelity bond
- Submit quarterly activity reports
Failure to register is a criminal offense punishable by fines or imprisonment.
Consumers and End-Users
Consumers now enjoy:
- Clear, simple financial information
- Better privacy protections
- Access to complaint and dispute resolution systems
Learn How to Open a Digital Bank Account in Nigeria.
Navigating Regulatory Changes
Fintech firms must:
- Use tools like Interpol’s financial crime monitoring
- Comply with data privacy rules from the National Data Protection Commission (NDPC)
- Train staff regularly on updated regulations
Compliance Strategies for Banks
Banks should:
- Implement Open Banking APIs
- Register platforms and exchanges properly
- Monitor transactions closely
Groups like ISACA and Alliance for Financial Inclusion (AFI Global) provide guidance.
Adapting Business Models
Payments and remittances remain the most popular fintech services. Open Banking enables fintechs to collaborate better and create innovative products.
Training and Awareness for Stakeholders
Regulators like the SEC and NDPC provide training resources. Fintech companies should regularly review their data handling and compliance practices. Organizations like CGAP offer consumer protection tools.
Implications for the Digital Economy
The ISA 2025 provides a solid legal foundation for Nigeria’s digital economy. It supports blockchain adoption and safer investment environments. This could encourage Nigerian capital held abroad to return, strengthening the local currency.
Fostering Innovation and Growth
With clear rules, fintech startups will likely increase. Young Nigerians may invest more in digital assets. Blockchain-based products will expand, driving further economic growth.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite progress, challenges remain. Bank systems sometimes lack full interoperability. Agencies like NIBSS and the NDPC work to resolve these issues.
Governance and Legal Considerations
Digital firms must:
- Follow International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
- Disclose operations transparently
- Register and submit reports to the SEC
Non-compliance can lead to license revocation or fines.
Disclaimers and Liability
Companies must:
- Protect user data per NDPC regulations
- Avoid aggressive loan practices under FCCPC rules
- Ensure truthful advertising to avoid misleading consumers
Preparing for the Future
ISA 2025 signals Nigeria’s readiness for digital banking growth. Tools like NRBVN and Open Banking enable safe expansion.
Roadmap for Participants in Digital Banking
Successful firms should:
- Monitor updates from SEC and NDPC
- Use global compliance guidance from AFI Global
- Review and improve KYC/AML systems regularly
Adapting to Evolving Regulations
The Nigerian fintech sector must stay agile. The ISA 2025 and Open Banking initiatives create new opportunities for growth and innovation. Staying compliant is key.
Conclusion: Thriving in Nigeria’s Maturing Regulatory Environment
The digital banking regulations Nigeria 2025 transform Nigeria’s fintech industry. By formally recognizing digital assets and strengthening consumer protections, Nigeria is poised to lead Africa’s digital finance revolution.
Banks, fintech companies, and consumers all stand to benefit from clearer rules, safer products, and more opportunities. With ongoing reforms, Nigeria aims to create an inclusive, secure, and innovative digital economy.


